The third molars, wisdom teeth, are the last molars at the back of your mouth.
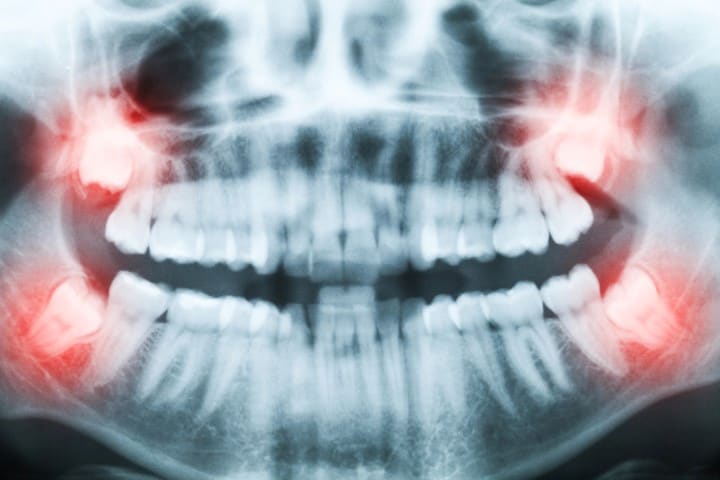
This type of molar usually erupts late into adolescence or early adulthood, denoting a maturity period between 17-25.
Definition of Wisdom Teeth:
The third set of molars, also known as wisdom teeth, was named because an individual gains some intelligence or wisdom in the development stage.
The typical number of wisdom teeth in humans is four, comprising two molars on each side of the top and bottom jaws.
Though these molars had a specific practical application for our ancestors eating less refined food, evolution and developmental changes in food preferences have reduced them to mere remnants of the former ones. A healthy adult usually contains four wisdom teeth.
Location in the Mouth:
The wisdom teeth are located at the back of the mouth in positions behind each corner, upper and lower.
The top wisdom teeth are located on the rear sides of the upper jaw, while the others are situated remotely in opposite parts at the lower jaw.
Because of their position, these molars can be difficult to clean well, so they may easily suffer from gum disease.

Timeline for Wisdom Tooth Eruption:
Usually, wisdom teeth erupt when an individual is entering adulthood or adolescence. However, interception is hindered by discomfort and swelling as possible complications such as impaction.
The sequence of wisdom teeth complications is very significant for individuals and dental professionals, paving the way for proactive management of potential eventualities with the goal that an individual maintains good oral health.
The Purpose of Wisdom Teeth
The history of wisdom teeth – also called the third molars is as intricate as it incorporates many evolutionary adaptations and alterations in how humans live today.
It is natural to look at their purpose from an evolutionary viewpoint, analyzing their role in history versus present times and assessing the level of implication that they play in the structure of teeth reveals essential information about these third molars.
Evolutionary Perspective:
From an evolutionary perspective, wisdom teeth were essential for early man since he had a harsh diet requiring sharp dentition to digest.
This dietary routine contained grounding and processed coarse foods such as roots, nuts, and raw meat.

The advanced jaws and worn-out teeth distribution of our ancient relatives made the third molars valuable to them so that a living could be ensured.
Function in the Past vs. Modern Times:
With human dietary development, progressive cooking and food processing distanced themselves from the need for stronger chewing. As a result, wisdom teeth lost the functional role that modern times.
The evolution of man has resulted in a decrease in arch size over generations due to diet changes, which subsequently increase the misrelation between several teeth versus tooth size, causing occlusal complications such as impaction or crowding.
Role in the Dental Structure:
Thus, though wisdom teeth may have abandoned their original function in consuming albuminous food, the mechanical effect they bring to the dental structure is not trivial.
Such molars may also help in orthodontic treatment that reflects some spacing. Nevertheless, the complexity of their after-effects, ranging from impaction to infection or malalignment, has created disparate views regarding their essential utility in modern dental treatment.
Common Complications with Wisdom Teeth
Recognizing the rudiments of potential concerns related to wisdom teeth is essential to ensure the optimal state of oral health.
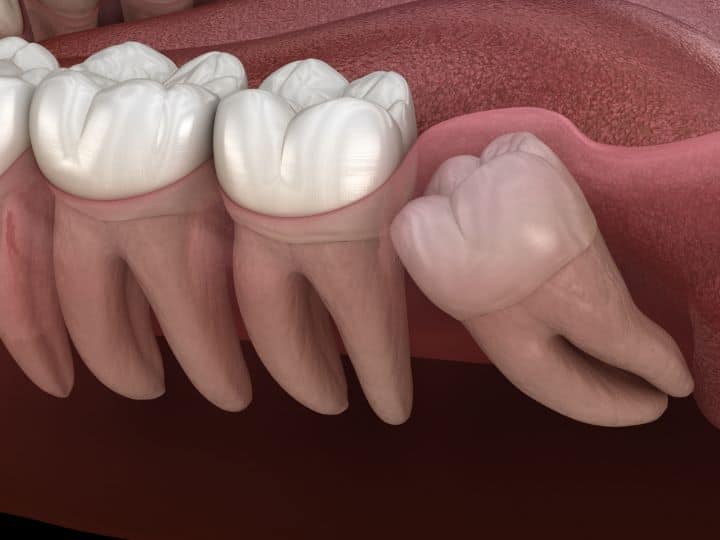
They cause problems – impaction, overcrowding, and infection- highlighting the necessity of eyed impacts on the occurrence or absence of perceptible molars.
Impacted Wisdom Teeth:
The most common issues affecting wisdom teeth development include impaction, where the molars do not erupt sufficiently through the gum.
This not only gives rise to several other complications, such as pain and inflammation, but it may also lead to damage associated with proximity teeth.
It is expected to have affected wisdom teeth remedied with removal to relieve discomfort and ensure subsequent adaptation.
Impacted wisdom teeth may be bothersome for you, but that is not always the case, and sometimes asymptomatic impacted wisdom teeth usually need no intervention.
Crowding:
Insufficient space at the rear of the jaw leads to crowding problems when wisdom teeth try their luck by erupting in a limited place.
Weight and pressure from these progressing molars may disrupt the proper alignment of existing teeth, thus causing misplacement and orthodontics issues.
Orthodontic analyses and even removal are often prescribed to eliminate problems with crowding.
Infection:
Infections can occur in the case of wisdom teeth, given that they are placed at the back of the mouth, where cleaning proves to be problematic.
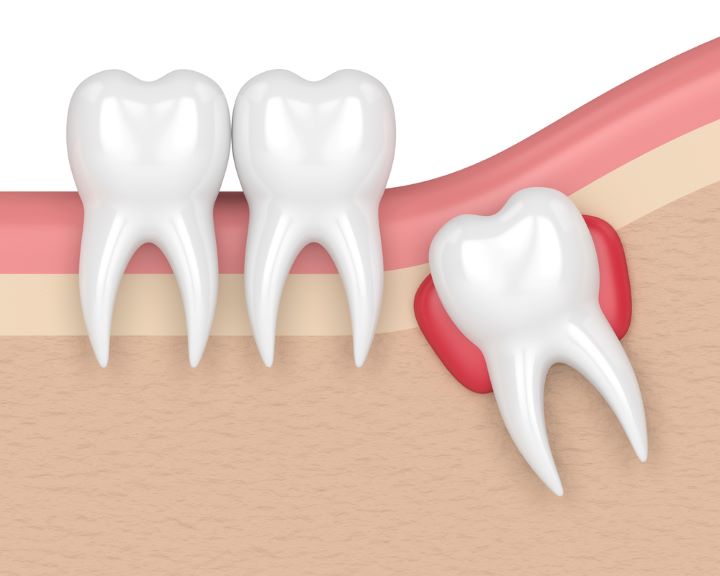
Unerupted wisdom teeth give birth to pockets, which are utilized by bacteria that build up infection and inflammation—known as pericoronitis.
Dry sockets, tooth decay, and maxillofacial deformities are some of the infection outcomes. Repeated diseases that are not good for oral health are perpetually suggested by dentistry professionals to be removed from the body, as we will understand shortly.
Signs and Symptoms of Wisdom Teeth Problems
Attaining appropriate awareness regarding the signs and symptoms of wisdom teeth problems is vital for early detection and effective management.
Pain, discomfort, and signs of swelling and redness indicate something is wrong with wisdom teeth. In addition, the inability to open the mouth widely signifies why a person may need to consult a dentist.
Pain and Discomfort:
Pain or discomfort in the lower part at the back of the mouth is one of the most prominent symptoms that indicate a harmful condition with wisdom teeth.
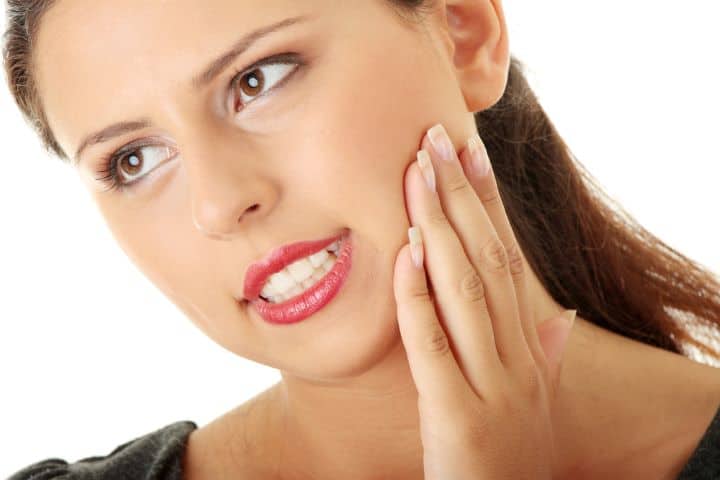

This pain may be a mild ache or severe, indicating impaction, infection, and crowding as possible leading problems. In the absence of the self, if there is persistent pain, people should visit a doctor to understand the source of pain.
Swelling and Redness:
There are some witch elements based on wisdom teeth problems that include the case of swelling and redness in the area.
The inflammation could be a reaction to impaction, infection, or irritations caused by unerupted molars only partially through the gum.
In addition to the initial pain level, swelling may increase discomfort and should be monitored closely as a signal that the surgical team might need to intervene or pull out.
Difficulty Opening the Mouth:
Another sign that may indicate wisdom tooth trouble is low jaw mobility or choking due to the inability to open the mouth completely.
When the wisdom teeth are compressed or misaligned, they are subject to pressure over surrounding tissues, leading to stiffness and less ability to move.
The inability to fully open the mouth persisting for a long time demands sound management history service by professionals who can find out what should be done about such
Treatment Options for Wisdom Teeth Issues
Solutions to wisdom teeth complications may vary depending on the patient’s conditions or problems with their health but are aimed at dealing with the issues one way or another.
The strategy includes multi-level monitoring from simple careful control to surgical intervention.
Monitoring and Observation:
Where there are no visible signs of any complications involving the eruption of the wisdom teeth, dentists can apply a fitting method that requires monitoring and observing these teeth.
By undergoing periodic dentition examinations by professionals, the dentist can monitor the growth of these molars, taking note of their potential effects on surrounding teeth.
Waiting and observing may be advised if the wisdom teeth pose no immediate danger.
Wisdom Teeth Removal:
One of the most popular and effective procedures for problematic teeth beneath third molars is pull-up.
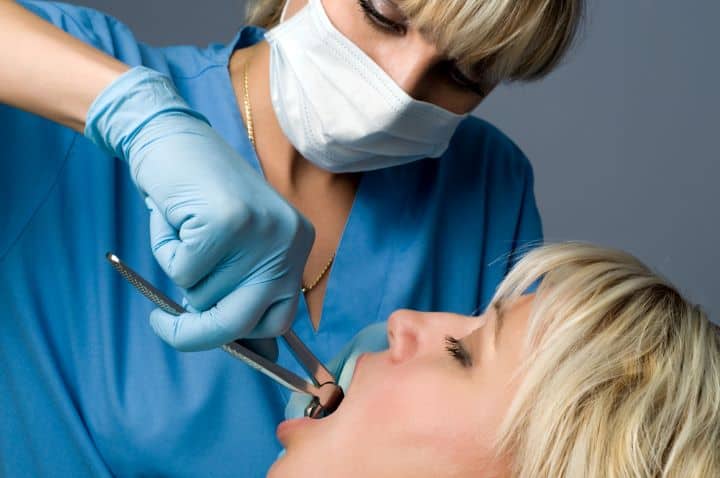
The procedure must be performed when jaws are impacted, misaligned, or in pain.
Extraction may be a simple, no-frills dental office procedure performed regularly, or it can be a complex surgery where both sides of one’s mouth are infused by an oral surgeon for heavily impacted molars lying deep below average root structure.
Pain Management and Recovery after Extraction:
After the surgery, pain management and getting back on one’s feet are considered fundamental aspects of this treatment process.
During the primary postoperative treatment, dentists commonly prescribe pain relievers to eliminate pains and other discomfitures.
In most cases, patients will be recommended to comply with specific guidelines regarding treatment, for instance, using ice packs, remaining at rest, and taking a soft diet.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts:
Routine surveillance and assessment coupled with early preventive dentistry find a place in determining possible moonlight dental issues associated with the emergence of wisdom teeth.
Awareness of warning signs and symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and difficulty opening the mouth, enables individuals to act promptly by seeking timely professional intervention, avoiding conditions or complications altogether, and contributing to overall oral health.
The treatment choices, ranging from watchful waiting to excision procedures, reflect some of the dynamics objectives that are key in comprehending wisdom teeth.
Although extraction is often utilized, each patient receives a tailored solution, which makes it challenging.
Treatment regimens around pain management and recovery protocols shed more light on the postoperative period, which is essential for aiding a good curing process.

In the end, wisdom teeth exist in a dialectical universe, as reflected by a historical assessment of current dental practices and a modern agency to oral hygiene.