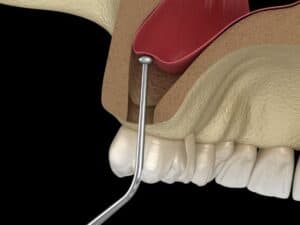
A tooth abscess is usually a painful and potentially serious dental condition caused by an infection of the concerned tooth or the surrounding tissues.
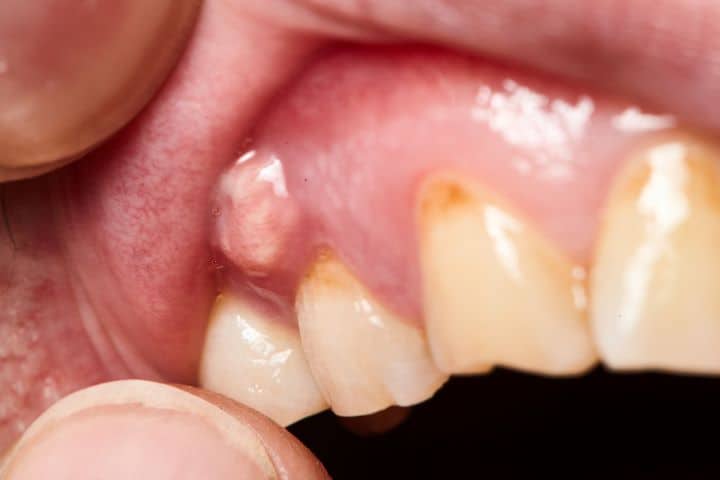
Infection causes pus accumulation, a mixture of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and other tissue debris.
Tooth abscesses can occur in various parts of the tooth and can lead to severe complications, so proper awareness, timely diagnosis, and management are of utmost necessity.
Definition of a Tooth Abscess:
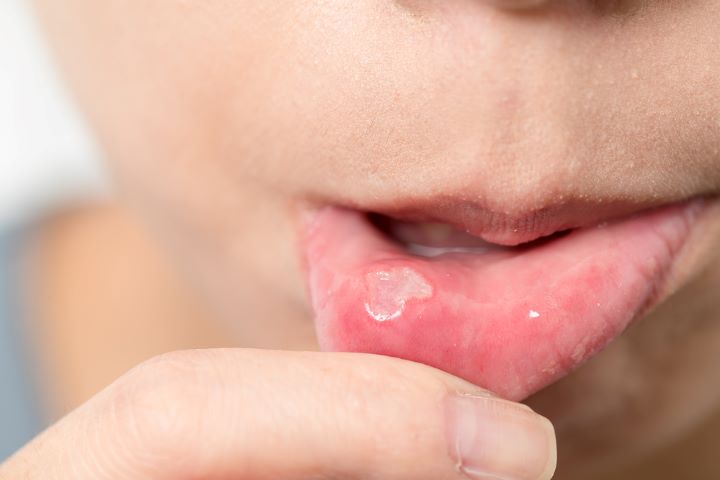
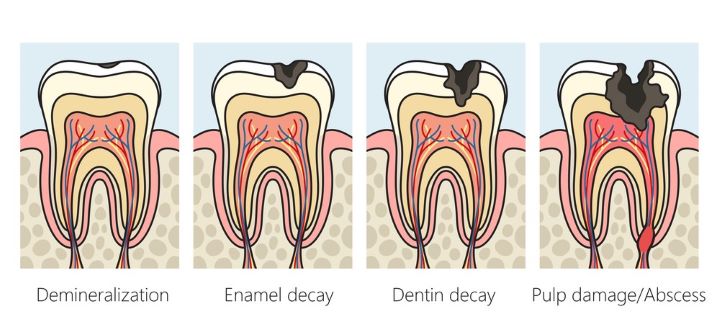
A tooth abscess is a pus-containing entity inside the tooth or other adjacent tissues. It responds to bacterial infection in the tooth and is often accompanied by inflammation and pain.
Infection can originate in the tooth’s pulp – its innermost part with nerves and blood vessels- or nearby gums. Pus accumulation within the confined space causes pressure, which may result in extremely painful, swollen, and possibly damaged tooth structure.
Types of Tooth Abscesses:
There are two types of tooth abscesses: periodontal abscess and periapical abscess.
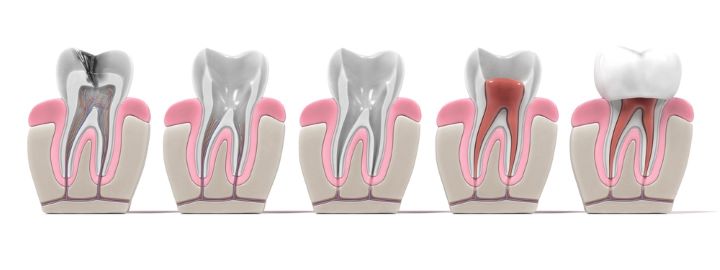
· A periapical abscess originates from an infection in the tooth’s pulp. It often occurs when bacteria invade the tooth through a cavity or crack, causing disease at the tip of the tooth’s root.
· Periodontal abscess is often associated with advanced gum disease (periodontitis) and develops in the gums and surrounding structures. This results from blockage of gum pockets, bacterial entrapment, or a severe infection.
Common Causes of Dental Abscess:
Bacterial infection is the leading cause of tooth abscesses. Poor dental hygiene, untreated cavities, lousy eating habits, and a compromised immune system can cause such infections.
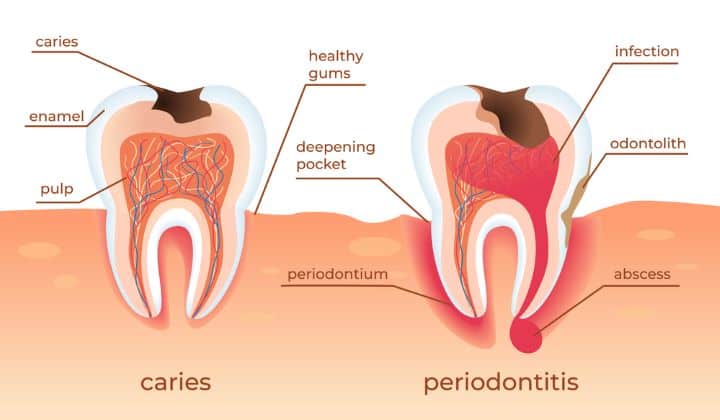
Other factors that increase the risk of tooth abscess formation include trauma to teeth, poor dental procedures, and a weakened immune system.
It is essential to identify these causes to take proper preventive measures and schedule appropriate dental care plans if any abscesses are found.
Signs and Symptoms of an Abscessed Tooth
A dental abscess is a severe dental problem that develops as bacterial infection occurs in the tooth or surrounding tissues. Identifying tooth abscesses’ signs and symptoms is vital to intervene early before matters worsen.
Pain and Discomfort:
A hallmark symptom of a tooth abscess is the persistent, throbbing pain. They usually worsen with time and may spread to the jaw, ear, or neck.
This pain is described as sharp or shooting and can decline by chewing or biting. Individuals with tooth abscesses often complain of the inability to find comfortable rest for an affected tooth, and the pain might even get so strong that it affects daily living.
Swelling and Redness of Teeth & Gum:
The affected site may be oedematous and painful. In some instances, the swelling may also involve the face or jaw, resulting in facial asymmetry. A visible sign of the body’s response to infection is manifested by redness around the offending tooth or in nearby gum tissues.
Sensitivity to Hot or Cold:
The sensation of thermic stimuli is usually hypersensitive in patients with a tooth abscess. Such sharp, shooting pains in the affected tooth may occur when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages.
This increased sensitivity is because the infection affects the dental pulp, which contains tooth nerves and blood vessels.
Fever and General Discomfort:
Systemic symptoms, including fever and lack of general well-being, can accompany a tooth abscess. The body’s reaction to the infection may increase body temperature, and people can feel fatigue, weakness, and general malaise. It is essential to monitor these general symptoms in order.
Complications of Untreated Tooth Abscess
Untreated tooth abscesses may bring severe problems beyond the oral cavity’s limits.
These potential complications should be comprehended to emphasize the need for early dental intervention.
Infection Spreading to Other Body Segments:
A significant risk in untreated tooth abscess is when the infection can spread to other parts of her body. The oral cavity is a highly vascularized and densely packed connective tissue system that serves as an entrance portal for bacteria owing to adequate access directly into the bloodstream.
Similarly, bacteria of the abscess can get into the blood and be transferred to distant organs for system infections. Typical areas where infection spreads are the brain, heart, and lungs.
This may lead to life-threatening complications such as brain abscesses, endocarditis, and pneumonia.
Bone and Tissue Damage:
Persistent infection within a tooth abscess will likely result in continuous bone and soft tissue damage. An infection may wear down the jawbone and lead to structural instability, undermining nearby teeth. Furthermore, the surrounding gums and facial tissues can get seriously damaged when severe cases occur.
Systemic Health Issues:
Untreated tooth abscesses do not just have localized issues; they can also cause systemic health problems. The infection-associated chronic inflammation may also worsen pre-existing conditions like diabetes or cardiovascular diseases.
In addition, the constant struggle of her immune system to fight against this infection can weaken its overall performance, leading to increased susceptibility in various other cases.
Diagnosis of Tooth Abscess
Early diagnosis and prompt tooth abscess treatment are crucial for your dental well-being. Here are a few modalities used by orthodontists for proper diagnosis of tooth abscess:
Dental examination:
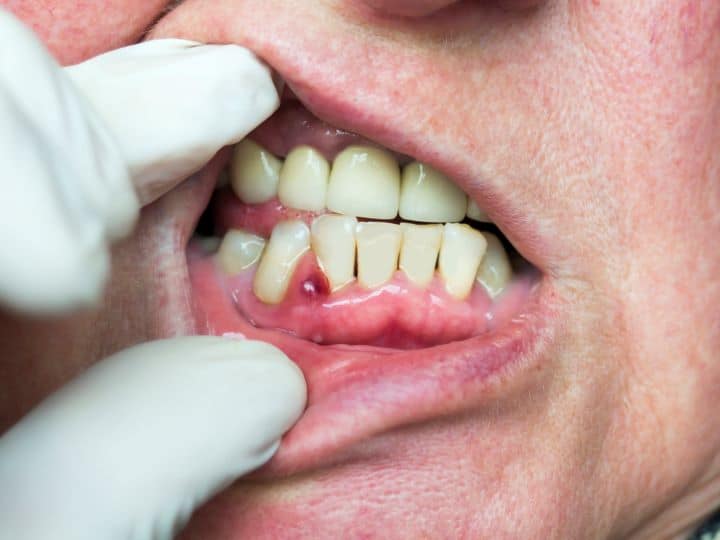
Dental examination constitutes the hallmark for the diagnosis of tooth abscess. It closely examines the gums, teeth, mouth, and oral cavity.
The affected tooth is tender to touch and may show signs of inflammation like swelling and redness. In a well-organized abscess, there may be pus discharge as well.
X-rays and Imaging:
Your dentist may order an X-ray to visualize the exact location and extent of infection, damage to the surrounding structures, and its impact on the tooth structure.
Other imaging modalities like CT scans can also be used to comprehend better the extent of infection and more exclusive and precise treatment plans.
Pulp vitality tests:
The pulp is the innermost part of the tooth containing its Neurovascular bundle. Pulp vitality tests check the pain response to a specific stimulus. This response can be divided into three categories:
§ Typical response: Where pain sensation is neither diminished nor exaggerated. It is the hallmark of a normal, healthy tooth.
§ Exaggerated Pain Response: In case of tooth abscess, the integrity of the neurovascular bundle may be compromised, leading to excessive sensations in your tooth.
§ Diminished Pain Response: the pain sensations are diminished in case of pulp necrosis or previous root canal therapy (RCT).
Here are the few tests that your dentist might use to check the pulp vitality:
· Thermal tests include heat and cold testing, although complex tests are more commonly used in daily practices. Something cold or hot touching the tooth will evoke sharp yet brief pain in your tooth, thus confirming the diagnosis of pulpitis and abscess.
· Electrical Pulp Testing: In this test, the mild electrical test is applied to the tooth to evaluate nerve function. It’s not commonly used.
· Percussion Test: The infected tooth is susceptible and tender to touch. In this test, the edge of the tooth is tapped, and the response is recorded.
Treatment Options for Tooth Abscess
Antibiotics:
Mixed flora comprising gram-positive, gram-negative, and anaerobes is involved in tooth abscess formation. Therefore, the exclusive use of oral antibiotics is the hallmark of treating tooth abscesses.
Antibiotics assist in infection control and symptom relief (such as pain, swelling, and redness) and halting the system’s spread of infection, thus preventing more grave complications.
Some antibiotics of choice are penicillin, amoxicillin, clindamycin, azithromycin, and metronidazole.
Drainage of the Abscess:
During drainage of the dental abscess, the oral cavity is first thoroughly rinsed with chlorhexidine oral solution, and topical or local anesthetic is applied.
Then, your dentist makes a small incision over the most dependent part of the abscess, and the exuding pus is removed via a gentle suction. This is followed by rinsing the area with normal saline. A small drain can also be placed for residual drainage in case of a larger abscess.
Root Canal Therapy:
Your dentist may opt for Root Canal Therapy (RCT) in case of suboptimal response to the antibiotics.
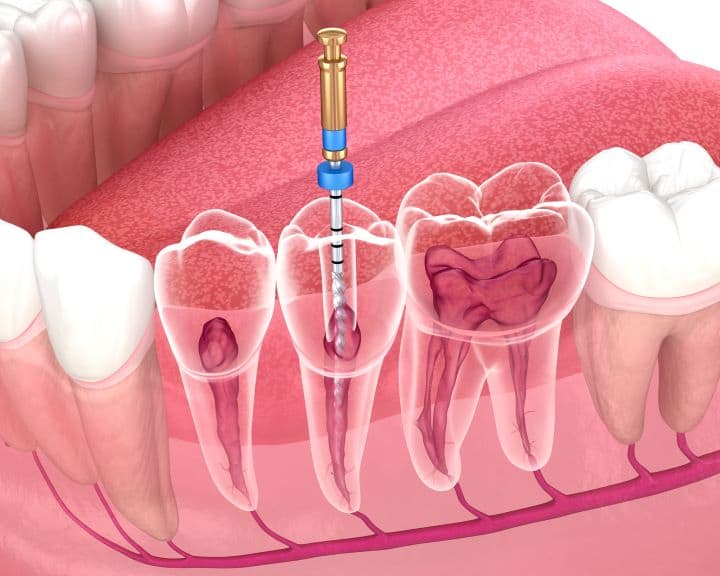
This procedure involves drilling into the root of your tooth, drainage of pus, removal of the infected pulp, sealing the area with specialized material (Gutta-Percha), and applying a temporary crown over the tooth.
Removal of pulp doesn’t compromise the functional integrity of your teeth, as its sole purpose is the detection of sensations.
Tooth Extraction
When the treatment modalities above fail, your dentist may propose tooth extraction as a last resort. Other indications for tooth extraction include extensive infection, risk of local and systemic spread, and tooth fracture below the gum line.
Home Remedies and Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most exclusively used over the counter for pain relief medications. They reduce the production of inflammatory mediators, thus reducing the pain due to inflammation.
In addition, they also assist in the reduction of swelling and redness. Acetaminophen is another choice that works to block pain signals in the brain.
Saltwater rinses
Saltwater rinses are very beneficial for toothache resulting from tooth abscesses. It reduces inflammation and swelling and helps in early recovery by cell migration.
Take one cup of Luke water and add 2 tablespoons of salt to it. Swish the solution in your mouth for 10-15 minutes every 6 hours.
Cold compress
Cold compress relieves pain by reducing swelling and inflammation. You can apply cold compresses with a bag of ice over the area for 10 minutes every few hours.
Preventing Tooth Abscess
Good oral hygiene Practices:
Good oral hygiene plays a pivotal role in dental and overall well-being. Following are a few steps you can take toward the betterment of your oral hygiene practices:
· Brushing: Brush your teeth twice daily (preferably after breakfast and before bed) with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
Avoid aggressive brushing and using a hard toothbrush. Additionally, regularly change your toothbrush every 3 months. The use of Florida-containing toothpaste also prevents tooth decay.
· Flossing: Gently floss your teeth daily to remove plaque or lodged food particles.
· Mouthwash: These help reduce bacterial overgrowth and strengthen your teeth.
· Tongue cleaning: It’s an often neglected aspect of oral hygiene practices. You can use a tongue scraper or even your toothbrush for this purpose.
· Good hydration and a balanced diet
· Avoid smoking and other tobacco products: These pose a threat to your dental well-being by increasing the risk of dental decay and oral cavity diseases. The risk of oral cavity cancer also increases fourfold, owing to the use of tobacco products.
Regular Visits to a Dentist:
According to NHS guidelines, you should have regular dental checkups twice a year in normal circumstances.

In case of any ailment, you can see a dentist more than that.
Avoiding sugary and Acidic foods:
Sugary and acidic products hurt dental health. Bacteria in your mouth feed on sugar and sugar-based products, thus increasing the risk of dental infections and decay. Similarly, acidic foods cause dental erosions over time by weakening the enamel of the teeth.
Therefore, consume sugary and acidic products in moderation for better oral health. Try incorporating fresh fruits, vegetables, and other healthier snacks into your daily routine.
Conclusion:
To conclude, an abscessed tooth is characterized by bacterial infections that cause the accumulation of pus and, without treatment, can lead to considerable complications.
Early intervention depends on recognizing the signs and symptoms, including persistent pain, swelling, sensitivity irritation, and systemic effects.
Complications of untreated abscesses are not limited to dental health; systemic infections and damage to bones and tissues can occur. Untreated cases also worsen existing illnesses.
Timely diagnosis through dental examinations and imaging and the appropriate treatment modalities, such as antibiotic drainage or root canal therapy, are equally important.
This includes a proper oral hygiene regimen, regular checkups, and a balanced diet that discourages consuming sugary or acidic foods.
With the right attitude, people can prevent difficulties like tooth abscesses while preserving good health. In case you are not feeling well, or have any dental issues or abscesses, you should see your dentist right away.