You’re at a point where, in addition to swollen gum tissues, you’ve started noticing other symptoms, too. You see your soft gingival tissue, which used to be firm and pink, pulled back away from the tooth, exposing the tooth roots.
Introduction to Periodontitis
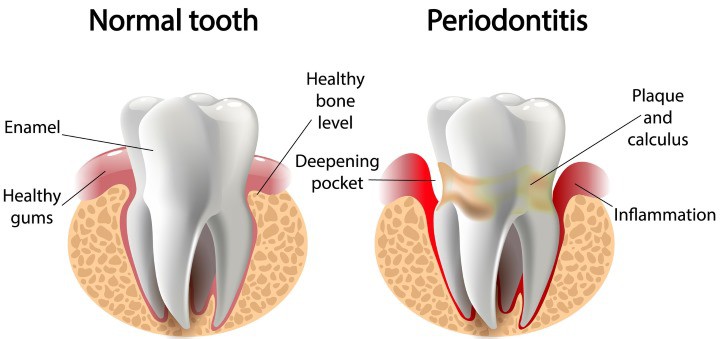
Periodontitis is a severe inflammation of gum tissues. When plaque and tartar accumulate around the teeth and above and below the gum line due to poor oral health conditions, the gums start to inflame.
They appear red and swollen initially and tend to recede over time. According to the National Institute of Dental Health, this creates a pocket between the tooth gum interface, providing more room for the bacteria to live in. Strep mutants and their friends live in the pockets, exacerbating the inflammation, which causes the body’s immune cells to intervene.
The fight between the bacteria and the immune cells causes destruction, which causes bone loss. All this makes your teeth go wobbly and loose in your mouth. The tissue and bone that supports your teeth become fragile, no longer holding the power to anchor the teeth. All this leads to tooth loss.
Did You Know A-Rod Has Gum Disease?
Baseball champion Alex Rodriguez (A-Rod) recently revealed that he was diagnosed with gum disease during his appearance on CBS Mornings.
He said, “Looks can be deceiving,” as he appeared with a bright smile that morning.
He further added, “I just recently went to see my dentist, not thinking anything about gum disease. And then the dentist tells me the news, and then I come to find out that over 65 million Americans have this gum disease. So it’s important for all Americans and all folks watching to go out and take care of their teeth. And better be safe by seeing your local dentist.”
Risk Factors For Periodontitis
Factors that put you at this risk of periodontitis are:
Smoking:
Smoking is the primary risk factor that leads to gum disease. The worst part is that most of the time, smokers don’t reveal the evident symptoms of gum diseases until it’s too late.
Diseases:
Diseases like AIDS, cancer, epilepsy, and diabetes are significant contributors to gum diseases. The medications taken to treat such diseases adversely affect the gums.
Genetic Susceptibility:
A few individuals are genetically susceptible to acquiring gum disease, no matter how adequate oral hygiene they have.
10 Causes of Periodontitis

There are a lot of factors that contribute to periodontitis. Know them all:
- Lack of proper brushing and flossing that leads to plaque buildup
- Never took professional scaling and root planing treatment for gum rejuvenation.
- Crooked or malaligned teeth make brushing and flossing difficult.
- Ill-fitting crowns, bridges, and dentures lead to food collection at the tooth-prosthesis interface.
- Smoking and chewing tobacco restrict the blood flow to the gums.
- Systemic diseases like diabetes cause delayed healing and dry mouth.
- Medications that cause dry mouth or gingival overgrowth.
- Hormonal imbalances due to pregnancy and use of contraceptives.
- Incorrect brushing techniques can cause damage to delicate gum tissues.
- Parafunctional habits like teeth grinding and clenching create deep pockets that harbor bacteria.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
According to the American Academy of Periodontology, you may face the following signs and symptoms if you have a gum disease, aka periodontitis:
- Swollen gums that are red in color and are painful, too
- The gums bleed whenever you brush, floss, or chew on hard things.
- Gum recession causes your teeth to look longer than normal.
- Teeth appear to be separated and have gams in between.
- Sores in your mouth.
- A change in the fit of the dentures you wear.
How Will Your Dentist Diagnose Periodontitis?
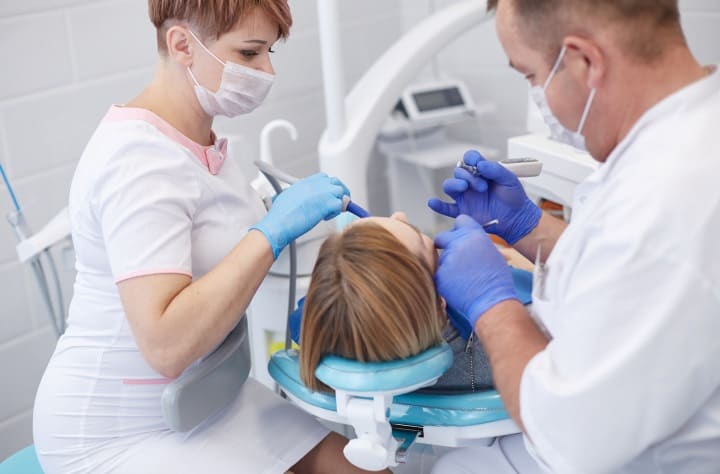
To assess the severity of periodontitis, your dentist will need to review you for the following:
Will Take A Complete Medical History
Your dentist will ask you for your medical history. He’ll question your symptoms and ask you for your social history. He’ll ask you about your brushing and flossing habits, too.
Oral Examination
Your dentist or dental hygienist will examine your mouth and see if your oral hygiene is properly maintained. He’ll look for plaque or calculus on the tooth surfaces and will look for any signs of gum inflammation. Moreover, he’ll examine your mouth for tooth mobility. Periodontitis is identified with a periodontal probe used to measure periodontal pocket depths along the long axis of the tooth. Typically, pocket depths are between 1 and 3mm. Deoth greater than 3mm signifies periodontitis.
Dental Radiographs
Radiographs or dental X-rays are carried out to look for bone loss. It could be generalized or localized.
Treatment of Periodontitis
The treatment of periodontitis can be broadly classified into non-surgical and surgical treatment options. Usually, a general dentist or a periodontist is the one you need to get you a perfect treatment plan to cure the condition. Advanced periodontitis is treated with both non-surgical and surgical therapy.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Scaling and Root Planing: With the help of ultrasonic devices, the calculus from the tooth surfaces and above and below the gum line is removed for gum tissue rejuvenation.
Antibiotic Therapy: Topical antibiotics in the form of gels are introduced into the deeper gum pockets to promote healing. Your dentist may also prescribe anti-bacterial mouthwashes to promote healing. Sometimes, oral antibiotics are also prescribed if dentists find signs like fever and swelling.
Surgical Treatment
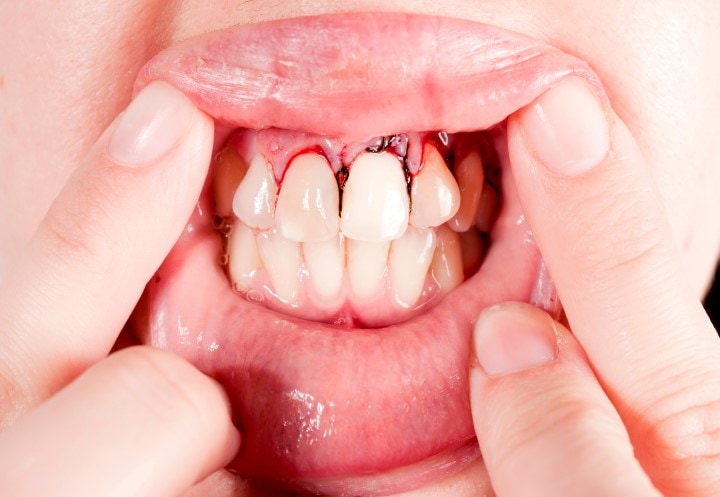
Pocket Reduction Surgery: Your periodontist will raise a flap, exposing your root surface. This procedure is followed by scaling root planing to remove the calculus from the root surfaces. The exposed flap is stitched back to a higher tooth level to eliminate the periodontal pockets.
Bone Grafting: When there’s a significant bone loss and a risk of tooth loss due to periodontitis, your periodontist may schedule a bone graft surgery. Either your bone will be grafted at the affected site, or a collagenous artificial bone will be used. The wobbly teeth will strengthen once the bone grows around it.
Guided Tissue Regeneration: Also known as GTR. Your periodontist will guide the growth of tissue by keeping a membrane at a tooth-tissue interface.
Prevention and Home Remedies
Prevention is always better than cure. How about you take care of your gums before it gets too late to save them? Adopt the following lifestyle and see how all odds turn into a favor.
- Brush twice a day with a soft-bristle brush with the right brushing technique. Stillman’s Technique is a popular brushing technique for individuals suffering from gum diseases.
- Rinse your mouth with water after every meal is one of the best ways to prevent periodontitis.
- Use electric toothbrushes.
- Floss once daily. You may use standard floss, super floss, or interdental brushes to aid the cleaning between the two teeth.
- Eat healthy. Maintain your good health by adding five parts of fruits and vegetables to your diet.
- Do not chew or smoke.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What are some of the common medications used to treat periodontitis?

| Medications | What Is It? | Why Is It Used | How Is It Used? |
| Prescription Antimicrobial Mouth Rinse | A mouth rinse that contains an antimicrobial agent called chlorhexidine. | To control bacterial growth in gum diseases. | Used as a regular mouthwash |
| Antibiotic Gel | An antibiotic gel containing doxycycline. | To get rid of bacteria living inside the periodontal pockets. | Your dentist will place it inside the pockets after scaling and root planing. |
| Antibiotic Microspheres | Tiny round spheres containing antibiotic minocycline. | To limit the growth of bacteria. | Placed in periodontal pockets by a periodontist. |
| Enzyme Suppressants | A low dose of doxycycline. | It keeps the destructive enzymes in check. | Available in tablet form. Use together with scaling and root planing. |
2) How to fix receding gums without surgery?
It’s possible to fix the preceding gums by adopting one of the few methods:
- Desensitizing agents: The exposed root surfaces cause generalized sensitivity. When desensitizing agents are applied to the exposed surfaces, they treat the nerve symptoms and help you maintain oral hygiene.
- Pink Porcelain or Composite: This material can mimic your gums. Your dentist can use this material to fill in the gaps between your teeth and the gums.
- Removable Gum Veneers: Made up of acrylic and silicone ma
3) How much will it cost to fix the receding gums in the United States?
| Procedure | Cost |
| Scaling and Root Planing | $100 to $1000+ |
| Gum Graft Surgery | $600- $1200 |
| GTR Therapy | $1600-$3200 |
| Veneers | $700-$1300/tooth |