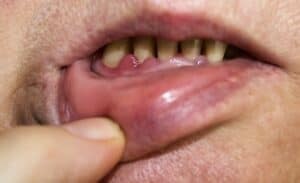
Our gums are supposed to be firm and have a light pink color. Gums that are irritated, bleeding, and red show signs of gum disease.
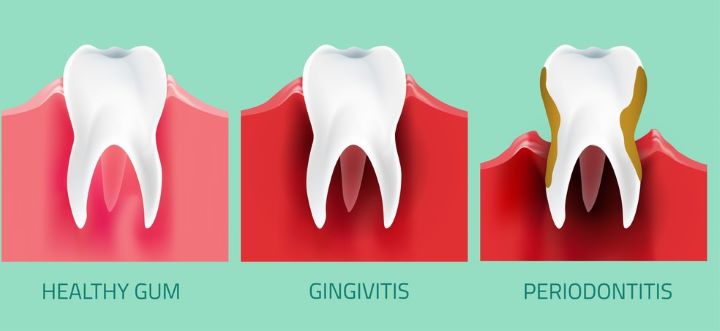
There are different stages of gum disease. Gingivitis is the milder form, while periodontitis is the severe one.
Let’s jump into the details because both gingivitis and periodontitis can be prevented, and ‘prevention is always better than cure.’
Gingivitis is a formulation of two terms: gingiva, the soft dental tissue, and -itis, which means inflammation.
The plaque forms whenever there’s a buildup of food and bacteria between the tooth and the gum line due to inadequate brushing and flossing. If the plaque isn’t removed for days, it turns into a white, hard, chalky material called calculus.
The plaque, tartar, and calculus together irritate the gingiva, causing inflammation.
But here’s the good news. Unlike periodontitis, a chronic condition, gingivitis is an early-stage gum disease. It’s reversible upon improving oral hygiene.
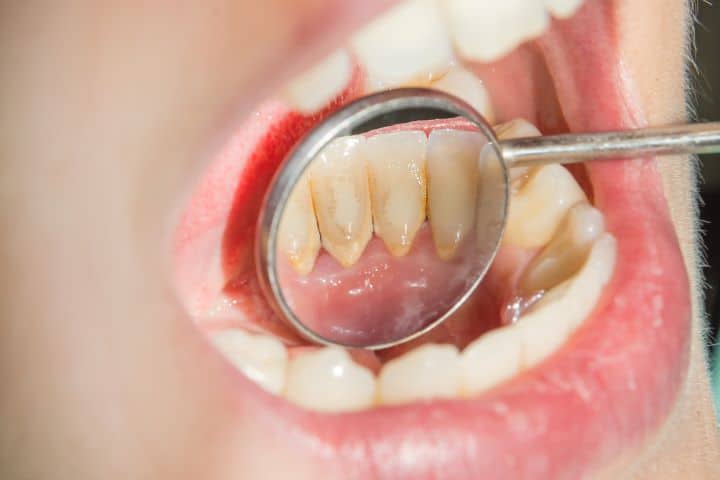
Contrary to this, periodontitis is the inflammation of the periodontium that includes periodontal fibers, bone, and the gingiva. The bacteria no longer stay above the gum line, but these nasty little individuals go deep into the tissue. This penetration of bacteria triggers a host response, ultimately leading to the destruction of the host tissue as well.
Periodontitis is irreversible, and it causes the loss of periodontal tissue, which subsequently leads to alveolar bone loss and, finally, teeth loss.
According to a CDC report, women are more prone to periodontitis than men in the US, and almost 47% of adults aged above 30 have some form of gum disease. Bad oral hygiene is the main cause of gum disease. However, some people with certain diseases are more susceptible to it. Without treatment can lead to tooth loss, the spread of infection to other teeth and other parts of the body (including the heart), and more.
Is this how you define your oral condition? Immediately see a dentist to save your teeth and gums on time.
How Gum Diseases Happen
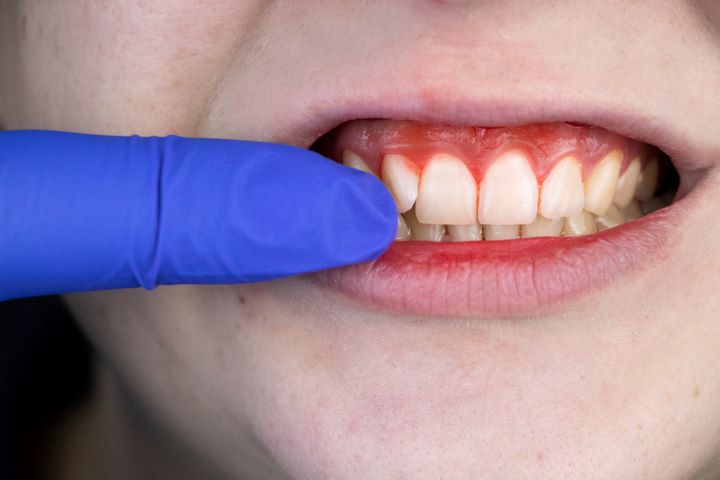
Our teeth are embedded into the bone with the help of a tissue called periodontium, aka the gum tissue. No matter how healthy you keep your teeth, the good health of your teeth depends on the healthy gum tissue to hold them in place.
The pink tissue that covers the teeth anchored in the bone is called the gums. Often, the gums get inflamed due to neglected oral hygiene, as seen when there is a plaque and a calculus buildup. This is called gingivitis.
Over time, the inflammation spreads deeper, affecting the periodontal tissue and the bone, which causes the teeth in your mouth to become wobbly. We call it periodontitis, which has different stages from mild to severe.
What are the Different Types of Periodontal Disease?
According to the American Dental Association, gum diseases can be classified into the following:
- Plaque Associated Gingivitis
- Gingivitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Disease
- Plaque Associated Periodontitis
- Early Onset Periodontitis
- Periodontitis Associated With Systemic Disease
- Necrotizing Periodontitis
What Causes Gum Diseases: Risk Factors For Gingivitis and Periodontitis?
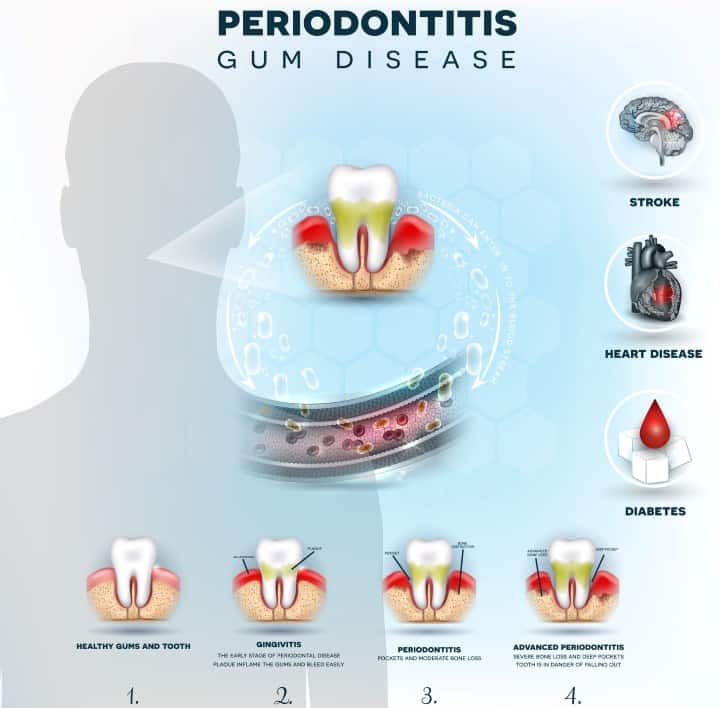
If asked what’s the main culprit behind the gum infection, the answer will be the dental plaque. However, other factors contribute to dental condition; knowing the risk factors help prevent the disease from happening at an early stage.
- Systemic Diseases: One of the significant systemic diseases contributing to periodontal diseases is diabetes mellitus. With high blood sugar, you tend to make less saliva, which causes more bacterial growth and plaque buildup. Autoimmune diseases also contribute to gum diseases, including lupus, scleroderma, and Crohn’s disease.
- Hormonal Changes: Why do women tend to have gingival disease? Hormonal changes are one of the reasons. The hormonal changes during puberty and menopause greatly affect gingival health.
- Smoking: Frequent smoking is a great contributor to gum infections. Smoking weakens the body’s overall immune system, desensitizing the body’s overall immune system.
- Stress: One of the potential risk factors is stress. With increasing stress, the body releases a high level of cortisol, a stress hormone that imbalances the inflammatory conditions in the body. Moreover, the increased stress levels in a person make him prone to habits like smoking or neglected oral hygiene, which worsens the situation.
- Diet: Less water intake, fewer fruits and vegetables in the diet plan, and frequent snacking can majorly contribute to the conditions called gum diseases.
- Certain Medications: Medicines like phenytoin, cyclosporine, and nifedipine can cause gingival diseases.
- Genetics: A rare but countable risk factor for gum diseases.
What Are The Symptoms of Gum Disease?
Symptoms of Gingivitis:
- Swollen gums
- Reddish gums appearance
- Bleeding gums
- Bad breath (halitosis)
Symptoms of Periodontitis:
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Unpleasant taste
- Gum recession
- Bone loss
- Pain on biting and chewing
- The gap between two teeth
- Wobbly teeth
How Does a Dentist Diagnose Gum Disease?
A regular dental check-up is essential to get an insight into your oral health from a specialist. A dentist can inform you well about your oral health and can warn you about the consequences of a condition if left untreated.
A dentist would closely examine the six surfaces of your tooth to assess the plaque, tartar, and calculus buildup. Moreover, they would check for the pocket depths with a periodontal probe to determine the severity of the gum diseases. The deeper the pockets, the poorer the condition.
A few investigations, like periapical x-rays and OPGS, are taken to reach a proper diagnosis.
A good clinician would also look for the root cause behind your oral condition and advise you to maintain oral hygiene apart from referring you to a periodontist for scaling and root planing therapy. Other advanced periodontal restoration procedures are also advisable, depending on the condition.
How to Treat Gum Disease?
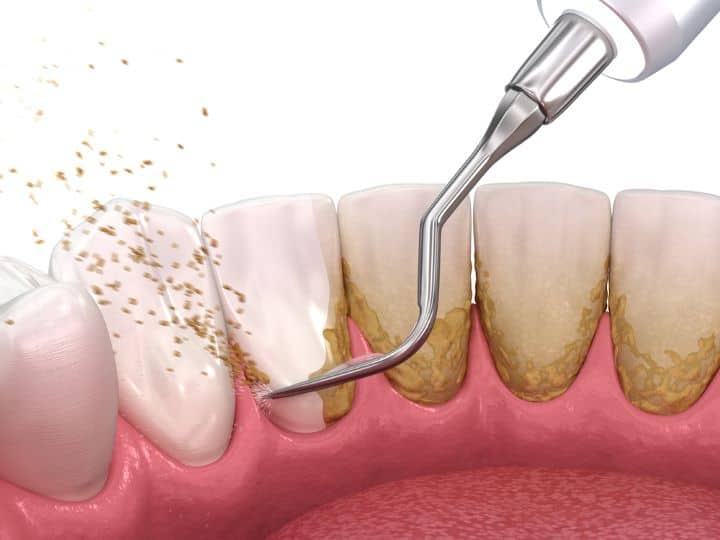
A multi-disciplinary approach is adopted for the treatment of gum diseases. First of all, maintain your overall health and oral hygiene by adopting good eating and brushing habits. Next, involve your dentist and see what treatment is needed to reverse your oral conditions. Here’s the list of treatments that your dentist or periodontist might suggest:
- Scaling & Root Planing: It’s more like routine dental cleaning. Ultrasonic scaling and root planing remove the calculus and stains from all the surfaces and the deeper surfaces of the tooth to say goodbye to the hub of harmful bacteria.
- Pocket Reduction Surgery: Pocket reduction surgery, also called osseous surgery, is meant to raise the gums and clean the tooth from the inside while repositioning the gums to a higher level with the help of stitches.
- Gum Graft: If your gums are lost, your periodontist would suggest a gum graft surgery. The surgeon would remove the oral tissue from the other part of your mouth to cover the exposed tooth roots to add thickness to the gum line.
- Guided-Tissue Regeneration: GTR is an artificial membrane that’s placed between your gums and the grafted bone to allow faster regeneration of the tissues and bone.
- Platelet-Rich Fibrin: PRP is majorly a part of your blood that’s centrifuged and infused at the needed area to allow rejuvenation and regeneration of the tissues. The growth factors present in the ultra-filtrate of your blood speed up the healing, leading to a quick recovery.
Can Gum Disease be Prevented: Tips to Optimize Oral Health?
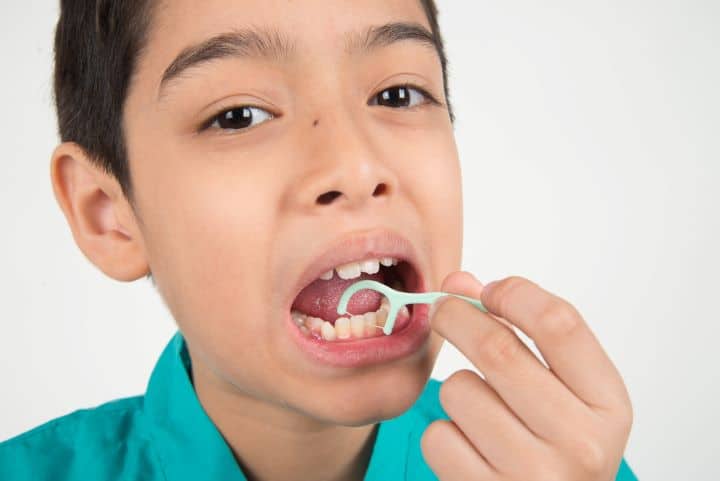
Preventing gum diseases and the health of tissue and bone is easy. All you need to do is to take care of your oral hygiene by following a few simple steps.
- Brush twice daily. Once in the morning after breakfast and once before going to bed.
- Floss once daily between your teeth and generally avoid poor oral hygiene.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash. Swish it once after you’re done with brushing at night.
- Avoid the frequent intake of fermented carbohydrates.
- Eat a good portion of everything. A balanced diet is a complete necessity.
- Avoid smoking and the use of tobacco.
- Rule out any comorbidity.
- Go for regular dental checkups regularly.
Complications Of Gum Diseases
Although gum diseases are very common among adults in the US, many of us fail to notice any symptoms unless the disease turns into an advanced stage. One of the major reasons behind it is, that gum diseases are painless initially. The best way to prevent gum infection or gingivitis is to get professional treatment as soon as you notice any symptoms. Or else you might face the complications which are listed below:
1) Tooth Loss: Our teeth are anchored into the bone which is covered with firm gingiva. As the disease progresses, you may experience bone loss which can ultimately lead to tooth loss. Tooth loss in adults has some adverse effects on esthetics, speech, overall health, and well-being.
2) Swollen gums: The early signs of gum diseases, especially gingivitis, include swollen gums. The gum irritation is expressed as an inflammatory response of the body, causing gingiva to appear red in color. Don’t worry! Gingivitis can be reversed once the plaque and tartar are removed from around the teeth professionally, and oral hygiene is maintained personally.
3) Chronic Bad Breath: Also called halitosis, it is associated with different stages of the disease. The bad breath is produced by the bacteria in the mouth that feed on the food particles sticking on and around the tooth.
4) Cancer: Advanced gum diseases predispose you to cancer, particularly lung cancer. It has been studied that advanced gum diseases increase the risk of cancer by about 24% when compared with healthy gums.
Can Gum Disease Cause Heart Disease?
If losing your teeth due to gum disease isn’t scary enough, so read this out. Research shows and proves that periodontal diseases increase the risk of heart disease, which includes heart attack and high blood pressure. Gum disease can also contribute to stroke, pneumonia, diabetes, infertility, and Alzheimer’s disease.
But the good news is that caring for your gums can minimize all the risks of the conditions mentioned.